-
Topics
subnavigation
Topics
Electromagnetic fields
- What are electromagnetic fields?
- Static and low-frequency fields
- Radiation protection relating to the expansion of the national grid
- High-frequency fields
- Radiation protection in mobile communication
Optical radiation
Ionising radiation
- What is ionising radiation?
- Radioactivity in the environment
- Applications in medicine
- Applications in daily life and in technology
- Effects
- What are the effects of radiation?
- Effects of selected radioactive materials
- Consequences of a radiation accident
- Cancer and leukaemia
- Genetic radiation effects
- Individual radiosensitivity
- Epidemiology of radiation-induced diseases
- Ionising radiation: positive effects?
- Risk estimation and assessment
- Radiation protection
- Nuclear accident management
- Service offers
-
The BfS
subnavigation
The BfS
- About us
- Science and research
- Laws and regulations
- BfS Topics in the Bundestag
- Links
Radon potential in Germany
Basis for the designation of radon areas
- For non-smokers, the radioactive noble gas radon is the most frequent cause of lung cancer.
- If high concentrations of radon are present in the soil and the soil is suitably permeable, radon can penetrate into buildings and build up there.
- The "radon potential" enables conclusions to be drawn about the risk of increased indoor radon concentrations. It links the gas incidence in the soil to its permeability to create an assessment parameter.
- The BfS has estimated the radon potential throughout Germany and has presented it as a map.
The radioactive noble gas radon can cause lung cancer. When radon is present in the soil in high concentrations and the soil is permeable, leaks in the building can cause a great deal of radon to enter the interior of buildings and accumulate there.
The concentration of radon escaping from the soil and its potential to penetrate into houses is known as the "radon potential". Its magnitude depends on two factors:
- How much radon is concentreted in the soil and
- How permeable (to gas) the soil is.
Radon potential: basis for the designation of radon areas
The radiation protection legislation (Strahlenschutzgesetz) requires regions with particularly high radon concentrations in indoor spaces to be designated as radon precautionary areas. In these areas
- the radon concentration in workplaces must be evaluated by taking radon measurements and
- measures for radon protection must be applied within buildings.
The radon potential of a region is an important basis for the establishment of radon precautionary areas.
Estimation of radon potential throughout Germany
Because every square metre of Germany cannot be measured for its radon concentration and gas permeability, the Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS) has developed a method to estimate the radon potential throughout Germany.
From 1995 to 2001, the radon concentration of the soil and its permeability was measured at around 3,700 locations in Germany. Using these values, the radon potential was also estimated for areas between these measurement points. Using geological knowledge, the measurement values were compiled into a map of Germany and then similar measurement values in regions close to one another were connected together. This template was then analysed and improved using mathematical simulations for the areas between the measurement points.
The method is based on procedures that are used in a similar form for the discovery of raw materials: Possible depositories are identified on the basis of a few sample boreholes. In earthquake research too, measurements and knowledge of subsurface geological properties are used to identify the potential earthquake risk of a given region.
Prognosis: regional radon potential
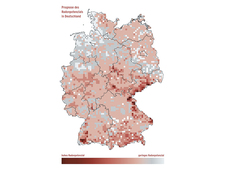
![]() Prognosis of radon potential in Germany
Prognosis of radon potential in Germany
The mathematical simulation methods have been used by the BfS to create a map of Germany in which the radon potential of regions is shown by colour.
The map provides an initial estimation of the radon situation in a region. The actual level of radon at a particular location can be assessed exactly only by taking air measurements close to the soil or by measuring the radon concentration within a building.
The map of radon potential in Germany allows the BfS to support the Federal Government and the states in developing a radon action plan to provide efficient strategies to protect against high indoor radon concentrations.
State of 2017.12.15


