As sunlight passes through the earth’s atmosphere, its intensity and spectral distribution are subject to changes caused by absorption, reflection and scattering. Most of the so-called "solar UV radiation", i.e. ultraviolet radiation from the sun, is absorbed by ozone in the stratosphere and troposphere. This filter function heavily depends on the UV wavelength.

The Federal Office for Radiation Protection (Bundesamt für Strahlenschutz, BfS) coordinates the interdisciplinary "UV Protection Alliance". The Alliance is a cooperation of well-known societies, organisations and authorities from radiation protection, medicine, science and occupational safety who are committed to UV protection for years. The Alliance advocates for a responsible handling with UV radiation. Objective of the Alliance is to reduce in the long term the number of new skin cancer cases and other adverse health effects caused by UV radiation.
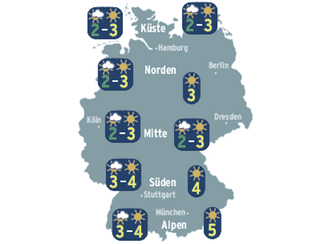
UV index forecasts are issued every 3 days each year from April to September by BfS, in cooperation with the Federal Environment Agency (Umweltbundesamt), Germany's National Meteorological Service (Deutscher Wetterdienst, DWD) and other associated institutions. The UV index is the internationally standardised measure of the daily peak value of erythemal UV radiation expected to reach the Earth’s surface. The higher the UVI value, the less time it takes for sunburn to occur on unprotected skin.

The sun is essential for life on earth. Many vital processes on the earth’s surface, such as climate and life itself, are fuelled by radiation energy from the sun. About 99.98 per cent of the overall energy accountable for the global climate originate from the sun

The Federal Office for Radiation Protection (Bundesamt für Strahlenschutz, BfS) advises that anybody who, despite the health risks involved, would like to use a sunbed should make a quality check on their own as a matter of principle. The “sunbed check” below provides a checklist suitable for this purpose.
The Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS) together with the Alliance for UV Protection initiated an interdisciplinary scientific expert discussion on the harmonization of the hitherto conflicting recommendations regarding UV exposure for endogenous vitamin D synthesis. The scientific discussion led to the following joint recommendation:
Typical UV Index values in various countries worldwide, calculated with the radiation transfer programme STAR at the 21st of each month.