-
Topics
subnavigation
Topics
Electromagnetic fields
- What are electromagnetic fields?
- Static and low-frequency fields
- Radiation protection relating to the expansion of the national grid
- High-frequency fields
- Radiation protection in mobile communication
Optical radiation
Ionising radiation
- What is ionising radiation?
- Radioactivity in the environment
- Applications in medicine
- Applications in daily life and in technology
- Effects
- What are the effects of radiation?
- Effects of selected radioactive materials
- Consequences of a radiation accident
- Cancer and leukaemia
- Genetic radiation effects
- Individual radiosensitivity
- Epidemiology of radiation-induced diseases
- Ionising radiation: positive effects?
- Risk estimation and assessment
- Radiation protection
- Nuclear accident management
- Service offers
-
The BfS
subnavigation
The BfS
- About us
- Science and research
- Laws and regulations
- BfS Topics in the Bundestag
- Links
The radon map of Germany
- The radon map of Germany provides orientation as to the regional distribution of the radon concentration in the soil air one meter below the surface.
- The calculation is besed on altogether 2,346 geologically representative measuring points and the geological map of Germany on a scale of 1:1,000,000.
- From this map it can be derived in which region and to what extent enhanced radon concentrations in buildings can be expected.
The radon concentration in the soil air is a measure of how much radon in the underground can get into a building.
Typically, the ratio of indoor radon to radon in the soil air is about one to five per thousand. That means that i.e. with an activity concentration in the soil air of 100 kilobecquerel per cubic meter, over 100 becquerel per cubic meter may occur in residential rooms in ten to fifty per cent of the buildings.
How probable the occurrence of enhanced radon concentrations is, depends among others on the time the building was erected and on the condition it is in.
Radon concentration in the soil air
The radon map of Germany therefore also provides indications as to in what regions enhanced radon concentrations in the soil air can be expected.
In less than one per cent of the buildings enhanced radon indoor concentrations can be expected in areas for which only radon concentrations in the soil air of less than 20 kilobecquerel per cubic meter have been forecast.
How to read the radon map
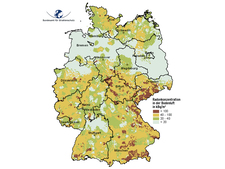
![]() Overview of the radon concentration in soil air at one meter depth
Overview of the radon concentration in soil air at one meter depth
The radon map of Germany serves to forecast the radon concentration in the soil air solely at regional level.
It is not possible to draw conclusions from the radon concentration in the soil air that has been forecast for a grid area to the radon concentration in the soil air at an individual site (such as a building plot) and, therefore, not to concentrations in a single building, either. This is due to the frequently small scale variations of the radon concentrations in the soil air and the different building designs.
- Radon concentrations of less than 20 kilobecquerel per cubic meter:
In areas with radon concentrations in the soil air of less than 20 kilobecquerel per cubic meter, the usual measures against soil moisture generally provide sufficient protection against enhanced radon concentrations.
These measures should be carried out carefully and with special focus on weak points (such as pipe lead-throughs). - Radon concentrations of more than 20 kilobecquerel per cubic meter:
In areas for which enhanced radon concentrations in the soil air have been forecast, the radon should be taken into account when constructing new buildings. Where appropriate, measurements of the radon concentration in the soil air should be carried out to evaluate a site.
To evaluate the situation in existing buildings located in such areas, it is recommended to carry out measurements of the indoor radon concentration.
Regional distribution
The radon map of Germany provides orientation as to the regional distribution of the radon concentration in the soil air in the pore space of the soil (soil air) one meter below the surface. Measurements at altogether 2,346 geologically representative measuring points carried out until September 2003 serve as data base. The density of the sampling was adapted to the geological variability.
In areas with higher geogenic radon potential and strikingly changing geology, the measuring points are closer to each other than in regions with medium to low radon potential. The comprehensive estimation of the radon concentration in the soil air was conducted by using a distance-weighted interpolation between the measuring points within generalised geological units based on a regular grid of three by three kilometers.
Expert application "BfS-Geoportal" shows Radon-222 in the soil air
Data for the prognosis of the radon concentration in the soil air can also be found in the BfS-Geoportal (in German only). This application enables to zoom in and to find out whether increased radon concentrations in the room air can be expected in your region.
Note: Having started the complex map application, first close the Welcome window. To show the place names in the map, move via drag and drop the layer "Radon-222 in Boden (Prognose)" in the legend (bottom right) below the Layer "Ortsnamen". If you click on the "+" at "Radon-222 in Boden (Prognose)" and move the slider to the left, you change the opacity/transparency of the map. In the same way, the visibility of the place names can be changed.
The actual levels of radon concentrations indoors can only be determined by measurements. Measurements can be carried out by e.g. laboratories offering radon measurements based on passive measuring devices in Germany that have proven to meet the quality assurance requirements.
State of 2018.02.27