-
Topics
subnavigation
Topics
Electromagnetic fields
- What are electromagnetic fields?
- Static and low-frequency fields
- Radiation protection relating to the expansion of the national grid
- High-frequency fields
- Radiation protection in mobile communication
Optical radiation
Ionising radiation
- What is ionising radiation?
- Radioactivity in the environment
- Applications in medicine
- Applications in daily life and in technology
- Effects
- What are the effects of radiation?
- Effects of selected radioactive materials
- Consequences of a radiation accident
- Cancer and leukaemia
- Genetic radiation effects
- Individual radiosensitivity
- Epidemiology of radiation-induced diseases
- Ionising radiation: positive effects?
- Risk estimation and assessment
- Radiation protection
- Nuclear accident management
- Service offers
-
The BfS
subnavigation
The BfS
- About us
- Science and research
- Laws and regulations
- BfS Topics in the Bundestag
- Links
Calculation of radiation exposure
- The radiation exposure to the population in the vicinity of every nuclear installation is calculated by means of the assessed discharges provided by the operator.
- The calculations relate to a reference person, a hypothetical individual, whose behaviour in regard to location and consumption habits results in the highest possible exposure to radiation.
- Reporting about the radiation exposure of the population which is determined from the activity discharges in exhaust air and waste water is a statutory duty. It is documented in the parliamentary report and in the BMU annual report "Environmental Radioactivity and Radiation Exposure".
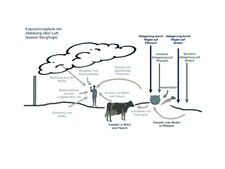
![]() Modelling of the transfer of radionuclides starting from the discharge of radioactive substances from the exhaust air stack through the biosphere to humans.
Modelling of the transfer of radionuclides starting from the discharge of radioactive substances from the exhaust air stack through the biosphere to humans.
By means of the assessed discharges provided by the operator the radiation exposure in the vicinity of every nuclear installation is calculated for a reference person. This reference person is a hypothetical individual, whose behaviour in regard to location and consumption habits results in the highest possible exposure to radiation (conservative assumptions).
Calculating radiation exposure using computer simulation
Dispersion models are used for the calculation. Using computer simulations, they calculate the transport processes of radionuclides from a nuclear installation into the various areas of the environment (see figure "Modelling of the transfer of radionuclides").
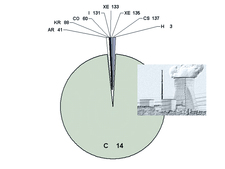
![]() Dose fractions of the radioactive substances discharged in exhaust air during the operation of nuclear power plants
Dose fractions of the radioactive substances discharged in exhaust air during the operation of nuclear power plants
The radiation exposure of the population can be determined from these concentrations of radioactive substances in the various environmental media (e.g. by means of the calculation model DARTM). In accordance with the Radiation Protection Ordinance, the exposure must not exceed
- 0.3 millisievert for the effective dose,
- 0.9 millisievert for the thyroid and
- 1.8 millisieverts for the bone surface
in one calendar year.
The greatest proportion of radiation exposure during normal operation is due to the radionuclide carbon-14 (see figure "Dose fractions of the radioactive substances discharged in exhaust air during the operation of nuclear power plants"). In this context, especially the intake of carbon-14 in the form of carbon dioxide through food (ingestion) is relevant to the dose.
Activity discharges in exhaust air

![]() Calculated effective dose of the reference person “adult” due to discharges in exhaust air (time period 1990 to 2016)
Calculated effective dose of the reference person “adult” due to discharges in exhaust air (time period 1990 to 2016)
Under conservative assumptions, the radioactivity discharges in exhaust air add up to a radiation exposure of
- less than 10 microsieverts in one calendar year for toddlers
- less than 5 microsieverts in one calendar year for adults.
These values are at significantly less than one per cent of the natural radiation exposure of the population (see figure "Calculated effective dose of the reference person "adult" due to discharges in exhaust air").
Activity discharges in waste water
The discharge of radioactive substances in waste water has been clearly reduced by high-performance systems for the treatment of waste water from nuclear installations.
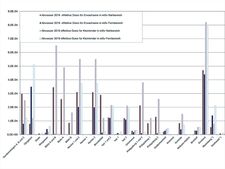
![]() Calculated effective dose of reference persons “adults” and "toddlers" due to discharges in waste water in 2016
Calculated effective dose of reference persons “adults” and "toddlers" due to discharges in waste water in 2016
Now, the calculated radiation exposure due to waste water is
- less than 2 microsieverts in one calendar year for toddlers
- less than 1 microsievert in one calendar year for adults (see figure "Calculated effective dose of the reference person “adult” due to discharges in waste water").
Reporting is a statutory mandate
The radiation exposure of the population determined from the activity discharges in exhaust air and waste water is documented in the parliamentary report and in the BMU annual report "Environmental Radioactivity and Radiation Exposure".
Environmental radioactivity and radiation exposure (Parliamentary Reports) since 2000show / hide
Since 1975, the German Cabinet has been reporting to the Bundestag on environmental radioactivity and radiation exposure. This so-called "Parlamentsbericht" ("Parliamentary Report") focusses mainly on anthropogenic radiation exposure from nuclear installations, medical use and special incidents in the scope of the Radiation Protection Ordinance.
According to § 5 paragraph 2 of the Precautionary Radiation Protection Act (StrVG), the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) is obliged to report to Bundestag and Bundesrat on a yearly basis on the developments concerning radioactivity in the Federal Republic of Germany. In order to do justice to the public discussions on possible health risks of new communication technologies, such as UMTS, the report also contains information about non-ionising radiation (NIR).
The reports from this series can be found in "DORIS", the BfS’s Digital Online Repository and Information System:
The reports are also published as "Bundestagsdrucksachen" ("Bundestag documents").
BMU reports on environmental radioactivity and radiation exposureshow / hide
The BMU's annual reports on environmental radioactivity and radiation exposure contain, among others, the results of the environmental radioactivity monitoring, the most relevant current data from the respective year(s) related to the development of environmental radioactivity and data concerning natural and anthropogenic radiation exposure in Germany. The reports also include information on non-ionising radiation (NIR) and on research projects in this area..
The reports from this series can be found in "DORIS", the BfS's Digital Online Repository and Information System:
State of 2018.03.12


